BY Nilowfer
Storage capacity is the big deal now a days. For example, before we purchase a mobile we look for a storage capacity due to number of applications and its usage and better performance. Same time it is required for us to understand how data is getting stored and secured, and maintained over the cloud.
The required physical space for storage of data with better economy and to save our engineers from the technical harassment of work– where cloud computing arises.
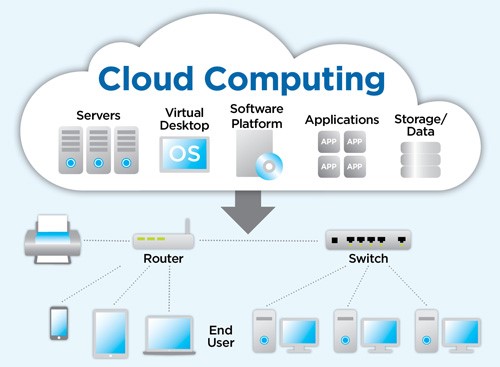
Cloud Computing is basically services hosted over the internet rather than onsite servers. Services can be accessed from remote locations over the cloud which saves time, cost, space and electricity.
Just like electricity which is not built and maintained in house, in the same manner the Cloud Computing also works. It helps companies in the consumption of the resources, like a virtual machine (VM), storage of data or an application.
Cloud computing mainly focuses on computing resources which are easily accessible, simple to use, cost effective and just to work. Cloud computing is not a singular technology, but it’s a way which delivers resources in such a way that helps in providing IT engineers self-service, on-demand and pay-per-use consumption. Cloud computing mainly saves time and money which is a big issue in IT world.
The Cloud basically comprises of the subscriber and the provider. The service provider can be a company’s internal IT group, a trusted third party or a combination of both. The subscriber is the one who uses the services. With the availability of data over the cloud it can be more easily accessed, with lower cost, increasing its value by enabling opportunities for enhanced collaboration, integration, and analysis on a shared common platform.
Finally we can say that, cloud computing consolidates major needs of today’s technological century: Autonomy with high agility and cost reduction, the best phrase that everyone likes to hear!
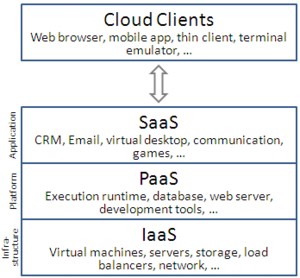
Types of Cloud Computing services:
• Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): A third party hosts elements of infrastructure, such as hardware, software, servers, and storage, also providing backup, security, and maintenance.
• Software as a Service (SaaS): Using the cloud, software such as an internet browser or application is able to become a usable tool.
• Platform as a Service (PaaS): The branch of cloud computing that allows users to develop, run, and manage applications, without having to get caught up in code, storage, and infrastructure and so on.
Types of Cloud:
There are mainly three types in cloud computing which are:
“Private, Public and Hybrid”
• A private cloud is like a purchase of own car, only one person can drive. In Cloud Speak, Space will be purchased by the organisation in which a limited access given within organizational boundaries. The Authorised engineers will be having an access to this private cloud with secured intranet, and this cloud – owned and controlled by organization. This cloud computing business model are purchased and managed by an organisation, in-house to enable shared IT services.
• A public cloud is basically the internet. The service providers use the internet to make resources, such as applications and storage, available to the general users, or on a public cloud. Some of the existing public clouds available today are Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2), IBM’s Blue Cloud, Sun Cloud, Google AppEngine and Windows Azure Services Platform.
• A Hybrid cloud is that in which companies can maintain a control over internally managed private cloud while relying on the public cloud as per requirement. For instance during peak hours some of the individual applications, or portions of applications can be migrated to the Public Cloud. This will also be beneficial during predictable outages: hurricane warnings or any other natural disaster.
Top benefits of cloud computing
1. Cost: Cloud computing saves us from the Money in investing for purchasing hardware or software and Manpower for setting up and running data centres, Space racks of servers & electricity for power and room with air condition for cooling and maintain room temperature & highly paid IT engineers for maintain and manage the infrastructure. It adds up fast.
2. Scalability: The advantage of cloud computing services include the ability to scale elastically. In other words, It delivers the right amount of IT resources—for example, more or less computing power, storage, bandwidth—right when it requires & over the world with everywhere, anyone can access.
3. Speed: Each cloud computing services are available with self-service and availability on demand, typically with just a minutes & few mouse clicks, gives a businesses with lot of flexibility and takes out our mental pressure while resource planning.
4. Productivity: On premises datacentres require a lot of space for racks with proper room temperature and proper planning, during software patching and maintenance of the data centre it requires for proper approval from the physical and company security, polices- which are directly proposal to the time-consuming IT managers. These tasks gets removed from the Cloud computing, so our IT teams can spend more time on business goals & can work productively.
5. Reliability: Cloud computing makes data backup with regular & on time, disaster recovery and business continuity easier and less cost effective, due to RAID.
6. Performance: The cloud computing services run on a worldwide connected network of secure datacentres, which are regularly updated/upgraded to the latest generation in time and with efficient computing hardware. This leads to the offers several advantages over a single corporate datacentre, which reduces the network latency for applications and for better performance.
Essentials of Cloud Computing Security
Although cloud computing offers small businesses significant cost-saving benefits—namely, pay-as-you-go access to sophisticated software and powerful hardware—the service does come with certain security risks. When evaluating potential providers of cloud-based services, we should keep security concerns in mind.
Just because all cloud service providers try to keep data safe, doesn’t mean they are all equally secure. With different budgets and specifications, each cloud service provider has a different flexibility level and security of data.
The cloud makes it easier for employees to access data, but at the same time, it’s important to define which employees get access to what data. But, the security of those data which is stored in cloud is very important. There comes in scene the Cloud Security.
Top 5 Security Risk involved in Cloud Computing
1. Secure data transfer: All of the traffic travelling between the network and whatever service is been accessed in the cloud must traverse through the Internet. It should be made sure that the data is always travelling on a secure channel; only connected to browser to the provider via a URL that begins with “https. Also, the data should always be encrypted and authenticated using industry standard protocols, such as IPsec (Internet Protocol Security), that have been developed specifically for protecting Internet traffic.
2. Secure software interfaces: The Cloud Security Alliance (CSA) recommends that to be aware of the software interfaces, or APIs, that are used to interact with cloud services. Reliance on a weak set of interfaces and APIs exposes organizations to a variety of security issues related to confidentiality, integrity, availability, and accountability.
3. Secure stored data: The data should be securely encrypted when it’s on the provider’s servers and while it’s in use by the cloud service. Some warns that few cloud providers assure protection for data being used within the application or for disposing of your data. We should be aware of potential cloud providers how they secure our data not only when it’s in transit but also when it’s on their servers and accessed by the cloud-based applications. We need to find out, too, if the providers securely dispose of your data, for example, by deleting the encryption key.
4. User access control: Data stored on a cloud provider’s server can potentially be accessed by an employee of that company, and he can have none of the usual personnel controls over those people. First, considering carefully the sensitivity of the data that are being allowed out into the cloud. Second, to ask providers for specifics about the people who manage the data and the level of access they have to it.
5. Data separation: Every cloud-based service shares resources, namely space on the provider’s servers and other parts of the provider’s infrastructure. Hypervisor software is used to create virtual containers on the provider’s hardware for each of its customers. But CSA have noted that attacks have surfaced in recent years that have targeted the shared technology inside Cloud Computing environments. So, investigation is required in the compartmentalization techniques, such as data encryption, the provider uses to prevent access into virtual container by other customers.
The main 12 cloud security threats:
• Data breaches: Cloud service provider implement their own security control but organisations are also responsible to secure their own data existing on the cloud.
Recommendation: Cloud service providers usually recommend to the organisation to use MFA & proper encryption algorithms/method to protect their data.
• Compromised credentials and broken authentication: Data breach attacks happens due to usage of weak password management & expired or third party certificates in use.
Recommendation: MFA systems such as one-time password, over call authentication, and usage of smartcard which will protect from attackers. Proper pen testing of the applications existing on the cloud, according to SANS or OWASP standards is recommended.
• Hacked interfaces and APIs: All the cloud services like the security and availability of authenticated passwords and encryption keys are dependent on the API. The high level of risk increases when a third party is involved which lead to exposure of the organisational credentials.
Recommendation: Strong interfaces and APIs expose organizations to security issues related to confidentiality, integrity, availability, and accountability.
• Exploited system vulnerabilities: A known vulnerability existing in the system or program, exploit are easily available to make it non-functional & which will impact on the business and reputation on the organisation. Fortunately, attacks on system vulnerabilities can be mitigated with basic IT processes.
• Recommendation: A regular vulnerability assessment, proper patch management, and regular follow-up on system against threats, dedicated resources.
• Account hijacking: Phishing-vishing, fraud ling, and system exploits are still successful, and cloud services add a new dimension to the threat because hackers can eavesdrop on activities, modify transactions & data. Hackers may also be able to get successful in lateral movement using one cloud application threat to another cloud application.
Recommendations: Organizations should prohibit the sharing of account credentials between users and services, as well as enable multifactor authentication schemes where available. Accounts, even service accounts, should be monitored so that every transaction can be traced to a human owner.
• Malicious insiders: The insider threat has many faces: a current or former employee, a system administrator, a contractor, or a business partner. The agenda for an insider to attack into an organisation may be data theft or revenge. In a cloud based scenario, an insider can destroy whole infrastructures or manipulate data. Systems that depend solely on the cloud service provider for security, such as encryption, are at greatest risk.
Recommendation: It is recommended that organizations control the encryption process and keys, segregating duties and minimizing access given to users. There should be periodic logging, monitoring, and auditing required.
• The APT parasite: It is called as Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs) “parasitical” forms of attack. APTs infiltrate systems to establish a foothold, then stealthily ex-filtrate data and intellectual property over an extended period of time. APTs typically move laterally through the network and blend in with normal traffic, so they’re difficult to detect. Recommendation: The cloud providers should apply advanced techniques to prevent APTs from infiltrating their infrastructure, but also the cloud service users need to be as diligent in detecting APT compromises in cloud accounts as they would in on-premises systems.
• Permanent data loss: In the cloud environment, reports of permanent data loss due to provider error have become extremely rare. But malicious hackers have been known to permanently delete cloud data to harm businesses, and cloud data centres are as vulnerable to natural disasters as any facility.
Recommendation: Cloud providers recommend distributing data and applications across multiple zones for added protection. Adequate data backup as well as adopting best practices in business continuity and disaster recovery. Daily data backup and off-site data storage is very important in the cloud based environment.
• Inadequate diligence: Due diligence applies whether the organization is trying to migrate to the cloud or merging with another company in the cloud. For example, organizations that fail to scrutinize a contract may not be aware of the provider’s liability in case of data loss or breach.
Recommendation: The organizations must perform extensive due diligence to understand the risks they assume when they subscribe to each cloud service.
• Cloud service abuses: The service providers need to recognize types of abuses such as scrutinizing traffic to recognize DDoS attacks and offer tools for customers to monitor the health of their cloud environments.
Recommendation: The cloud service users should make sure providers offer a mechanism for reporting abuse. Although the users may not be direct prey for malicious actions, cloud service abuse can still result in service availability issues and data loss.
• DoS attacks: DOS Attack is a malicious attempt by a single person or a group of people to cause the victim, site or node to deny service to its customers. DoS is when a single host attacks and DDoS is when multiple hosts attack simultaneously. Purpose is to shut down a site or to make service unavailable, not penetrate it.
Recommendation: Cloud providers tend to be better poised to handle DoS attacks than their customers. The key is to have a plan to mitigate the attack before it occurs, so administrators have access to those resources when they need them.
• Shared technology, shared dangers: The cloud service providers share their infrastructure, platforms, and applications, so if there is any vulnerability in any of these layers, it affects everyone in the network. A single vulnerability or misconfiguration can lead to a compromise across an entire provider’s cloud.
Recommendation: It is recommended that a defence-in-depth strategy, including MFA on all hosts, host-based and network-based intrusion detection systems, also applying the concept of least privilege principle, network segmentation, and patching of the shared resources.
References:
www.infoworld.com
www.blogs.cisco.com
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cloud_computing_security
https://cloudsecurityalliance.org